This article comprehensively analyzes the definition of DDoS attack, four main types (UDP Flood, SYN Flood, HTTP Flood, DNS Amplification) and their defense technologies, including fire protection...

DDoS's full name Distributed Denial of Service, which is a simple and crude attack. It aims to paralyze the target website (server) by sending huge traffic exceeding its processing capacity to the target website (server) and preventing it from providing services to users.
Its core logic is:
This is like having a restaurant (website) that can provide takeaway delivery (content) services to 100 people (networkers) at the same time under normal circumstances. Suddenly, 10,000 strange customers (DDoS attack source, commonly known as "brutch chicken") came, maliciously placed 10,000 orders for takeaway delivery (DDoS attack request), and canceled within a few minutes, making the restaurant tired of dealing with it, making it difficult or even unable to provide services to normal customers.
How to prevent DDOS attacks
Black Hole Routing
First, let's introduce the first defense method - black hole routing. As the name suggests, when a DDoS attack occurs, in order to prevent the impact from further expanding, the customer network informs the operator network of a black hole route about the attacked server IP. After the operator network receives the black hole route, it stops informing the IP route. At this time, the attacked IP address seems to have disappeared from the Internet and cannot be accessed by any host - it is equivalent to creating a "black hole" of routes on the Internet.
To facilitate your better understanding, the author gives you an example. As shown in the figure below, there are four servers A, B, C, and D in the customer network, sharing the Internet access services provided by a certain operator. Suddenly, Server A was attacked by DDoS from the Internet, and Server A was soon paralyzed due to excessive load and could not provide services to the outside world. What's more serious is that due to the continuous surge in attack traffic, the Internet exports connected to the customer's network also experienced serious traffic congestion, which made it impossible for unattacked servers B, C and D to provide services to the outside world normally.
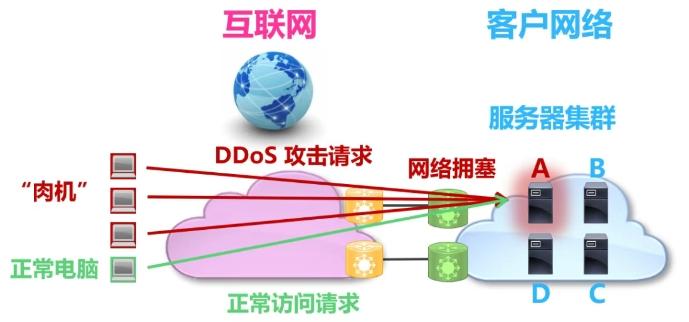
Picture: DDoS attack diagram
At this critical moment, the customer network yelled at the upstream operator: "Server A is dead!". After the operator received the message, he also shouted from all directions of the Internet: "Server A is dead, don't look for him through me!" So, one passes to ten, ten passes to hundreds, and the news of Server A's death spread throughout the Internet.
In this way, all hosts on the Internet, including "meat machines" and normal computers, cannot find Server A. DDoS attack traffic and normal traffic are discarded at the edge of the Internet, and the network congestion is also lifted, as shown in the figure below.
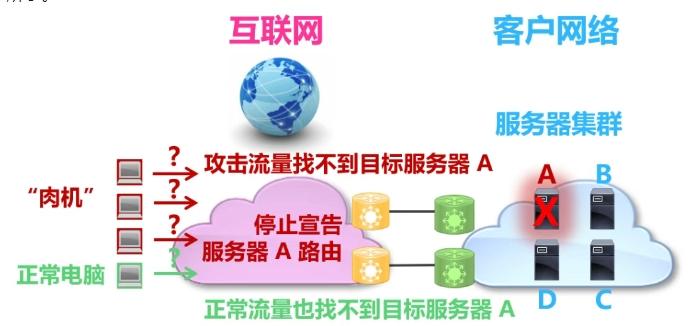
Picture: Schematic diagram of the working principle of black hole routing
This is how black hole routing works. Careful readers may find that the side effects of black hole routing are very large because normal traffic is also affected. Therefore, the essence of using black hole routing to defend DDoS attack is to "abandon the car and protect the coach", and to protect the customer network by sacrificing the attacked server and relieving network congestion.
Advanced Protection
Although black hole routing effectively stops DDoS attacks, it has significant side effects after all. Are there any side effects that are less defensive? The answer is advanced protection.
As shown in the figure below, advanced protection needs to be achieved through the cleaning center. It works as follows: First, the cleaning center is connected to the Internet through extremely large bandwidth, which can promise large-scale DDoS attacks; second, the cleaning center deploys traffic analysis and filtering equipment, which can distinguish attack traffic from normal traffic and filter attack traffic; further, the cleaning center is similar to an intermediary, which will inform the Internet of routes to the customer network and lead traffic to itself. In this way, when a DDoS attack occurs, the cleaning center can use its powerful bandwidth capacity and traffic analysis and filtering capabilities to "withstanding" the attack, and only send normal access requests to server A, thereby protecting both server A and the entire customer network.
In layman's terms, the cleaning center is like a bodyguard and agent of the customer's network. All traffic that needs to access the customer's network needs to pass through the bodyguard. A bodyguard with high martial arts can block all uninvited guests for the customer and only let the good people go.
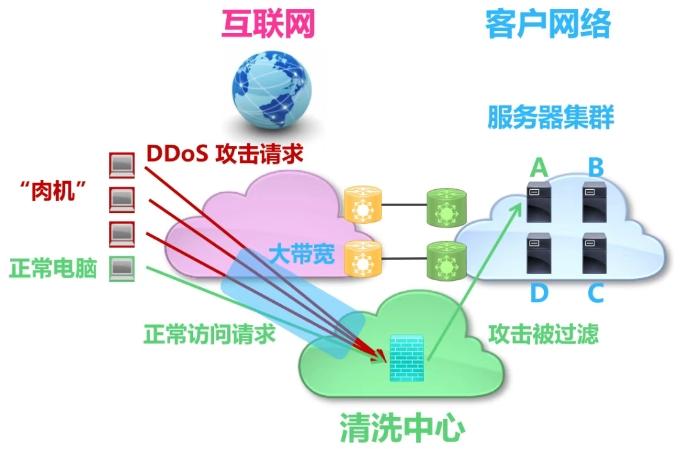
Picture: Schematic diagram of the working principle of advanced protection
Use advanced protection to fight DDoS attacks is the essence of "using resources for security", and "hardly shouldering" DDoS attacks through large bandwidth networks and high-performance traffic analysis and filtering systems. In addition, advanced protection extends the path of traffic and introduces cleaning centers, which will increase the latency of the business to a certain extent and may affect the user's access experience.
near source cleaning
Although advanced protection can effectively protect the attacked servers and customer networks, it comes at the cost of consuming bandwidth resources and computing resources. Is there a smarter way to save resources? The answer is near source cleaning.
As shown in the figure below, near-source cleaning is achieved by the edge network of the cleaning dispatch center and the operator. Its working principle is as follows: the cleaning and dispatching center will conduct real-time monitoring and analysis of traffic on the Internet. Once the DDoS attack traffic is discovered, it will guide it to the nearby edge node for distributed cleaning, suppressing the DDoS attack from the source, achieving the effect of "small money from four or four".
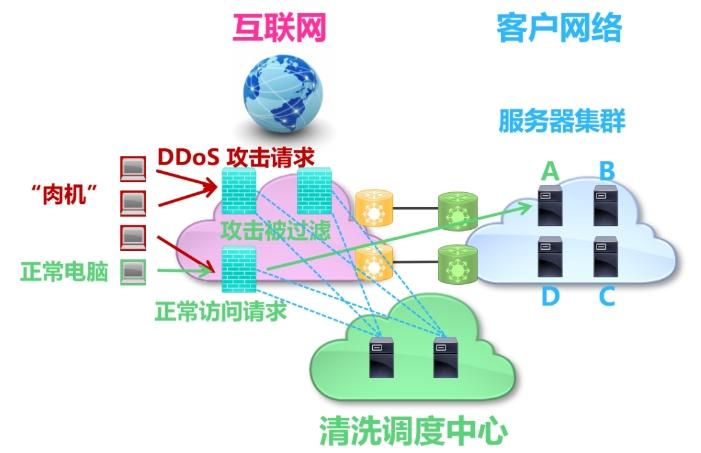
Picture: Schematic diagram of the working principle of near-source cleaning
It should be pointed out that near-source cleaning requires "cloud-edge collaboration" to achieve, that is, not only must there be the ability to analyze traffic, but also the network equipment that can schedule the edge to filter traffic. Therefore, near-source cleaning is a unique advantage of operators. It is therefore limited to the autonomous domain of the operator's Internet - because one operator cannot schedule another operator's network equipment.
Summary
Black hole routing, advanced protection and near-source cleaning are currently three effective means of defense against DDoS attacks in the industry. Due to the different performance effects, applicable scenarios and product tariffs, customers can selectively use them as needed.
For the convenience of viewing, the author has made the following table listing the characteristics of various DDoS defense methods.
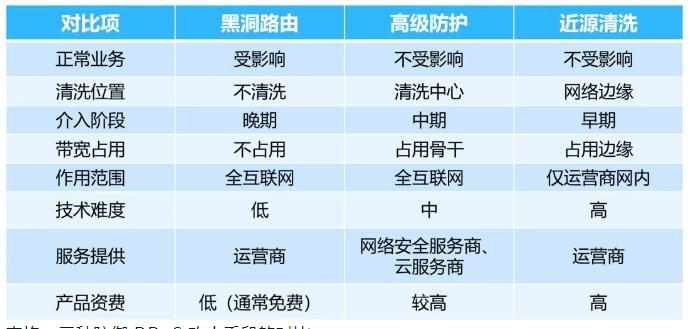
Table: Comparison of three types of defense DDoS attack methods
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: How to determine whether you are suffering from DDoS attacks?
Check server resource utilization immediately (CPU, memory, bandwidth)
Check for large number of abnormal requests in the access log
Use iftop or nload to view real-time traffic distribution
Login to the cloud console to view DDoS protection reports
Q2: How much does it cost to defend against DDoS?
Basic protection: cloud manufacturers provide basic free packages (usually below 5G)
Enterprise-level solution: on-demand elastic protection (billed by attack traffic, about 200 yuan/G/month)
Hardware equipment: a single D device is about 50,000-500,000 yuan (depending on the protection capability)